Pain with Internal Rotation of Shoulder: Understanding, Treatment, and Prevention
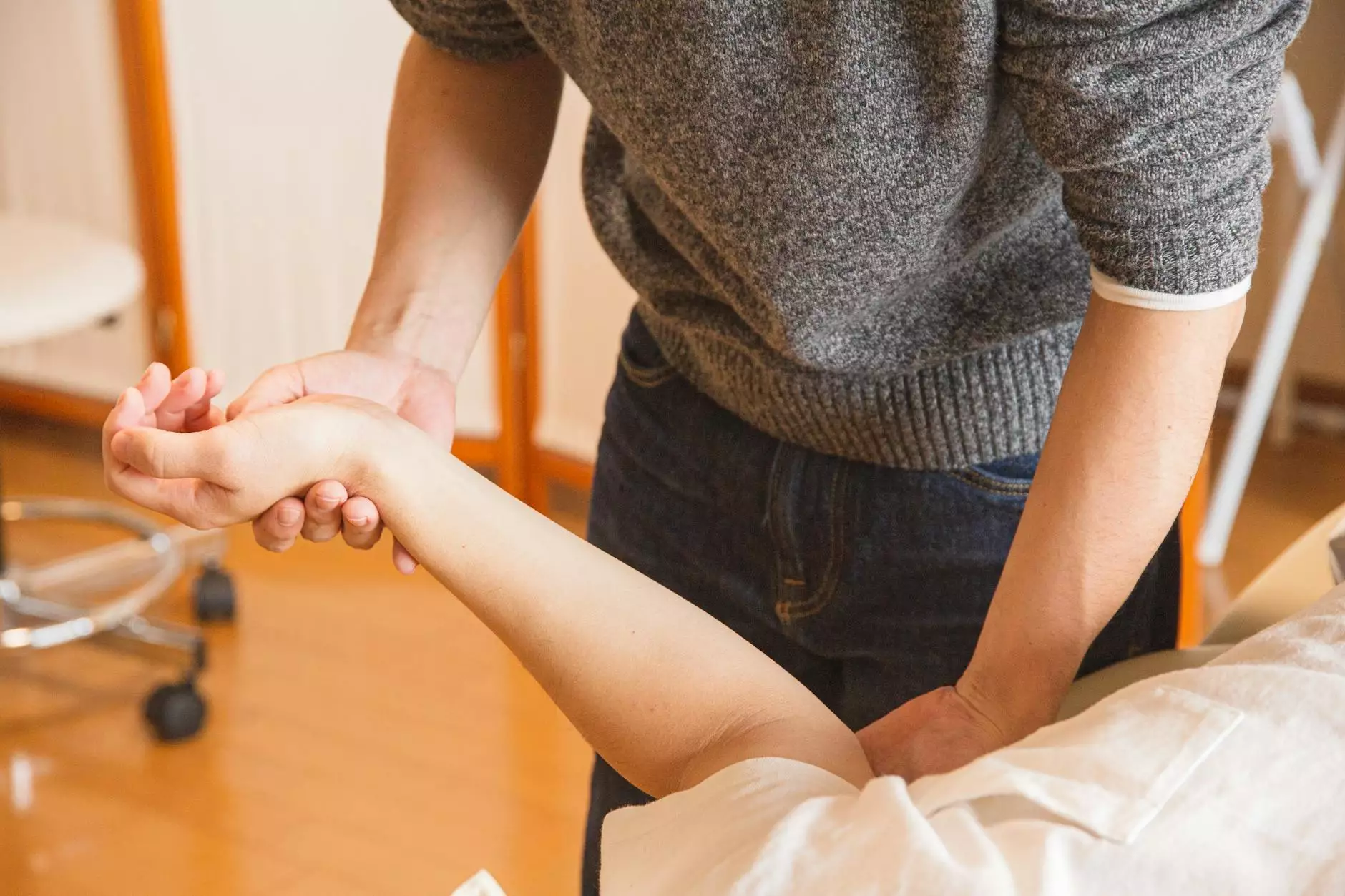
The shoulder joint is a remarkable structure that enables a wide range of motion, essential for daily activities and sports. However, when experiencing pain with internal rotation of the shoulder, many individuals find their capabilities limited. This article aims to provide in-depth knowledge regarding this condition, its causes, symptoms, treatment options, and preventive measures.
What is Internal Rotation of the Shoulder?
Internal rotation of the shoulder occurs when the arm is rotated inward. This movement is crucial in various activities like throwing, reaching behind the back, or performing everyday tasks. However, when internal rotation leads to discomfort or pain, it may indicate an underlying issue.
Common Causes of Pain with Internal Rotation of Shoulder
The causes of pain with internal rotation of the shoulder can be multifaceted. Here are some common contributors:
- Rotator Cuff Injuries: Rotator cuff tears or tendinitis can significantly restrict movement and cause sharp pain during internal rotation.
- Shoulder Impingement: This condition occurs when the rotator cuff muscles are impinged during shoulder movements, leading to pain and inflammation.
- Frozen Shoulder (Adhesive Capsulitis): Characterized by stiffness and pain, a frozen shoulder can make internal rotation particularly painful.
- Labral Tears: Injuries to the cartilage (labrum) that stabilize the shoulder socket may result in pain and a clicking sensation during internal rotation.
- Subacromial Bursitis: Inflammation of the bursa located under the acromion can prompt discomfort during specific shoulder movements, including internal rotation.
Recognizing Symptoms
Understanding the symptoms associated with pain with internal rotation of shoulder is crucial for early intervention:
- Local Pain: Pain localized in the shoulder, especially during internal rotation.
- Weakness: A noticeable decrease in strength when lifting or rotating the arm.
- Stiffness: Difficulty in moving the shoulder freely, particularly in internal rotation and overhead activities.
- Swelling: In some cases, the shoulder region may appear swollen or inflamed.
- Creaking or Clicking: Sensations of creaking or clicking sounds may accompany movement as a result of joint irregularities.
Diagnosis and Assessment
If you experience persistent pain with internal rotation of shoulder, it is essential to consult a healthcare professional. During the assessment, the following methods may be employed:
- Physical Examination: A thorough assessment of shoulder mobility and strength through specific movements.
- Imaging Tests: X-rays, MRIs, or ultrasound may be ordered to visualize structural anomalies or injuries.
- Functional Tests: Assessing how the shoulder performs specific tasks can help pinpoint the source of pain.
Treatment Options for Shoulder Pain
Treating pain with internal rotation of the shoulder often involves a combination of approaches based on the underlying cause:
Conservative Treatments
- Rest: Taking a break from activities that exacerbate the pain is fundamental.
- Ice Therapy: Applying ice packs can help reduce swelling and alleviate pain during the initial stages of injury.
- Physical Therapy: Customized exercises designed to improve strength, flexibility, and range of motion can be incredibly effective.
- Anti-inflammatory Medications: Over-the-counter medications like ibuprofen may reduce pain and inflammation.
Advanced Interventions
- Corticosteroid Injections: In cases where pain is severe and persistent, injections may provide temporary relief.
- Surgery: For significant tears or impingement, surgical options may be considered to repair or decompress the affected areas.
Rehabilitation and Recovery
Post-treatment rehabilitation is critical for effective recovery. A physical therapist can develop a structured rehabilitation program that may include:
- Range of Motion Exercises: Gentle stretches to improve flexibility and function.
- Strength Training: Targeted exercises to strengthen the shoulder muscles, particularly the rotator cuff.
- Functional Training: Activities that mimic daily tasks to prepare the shoulder for normal activities.
Preventive Measures
Preventing pain with internal rotation of the shoulder can significantly reduce the risk of injury. Here are some effective strategies:
- Warm Up Properly: Always take time to warm up before engaging in sports or activities that involve shoulder movement.
- Maintain Good Posture: Practicing good posture helps minimize shoulder strain.
- Incorporate Shoulder Exercises: Regularly engage in exercises that strengthen the shoulder muscles and improve range of motion.
- Avoid Repetitive Motions: If your job or activity involves repetitive shoulder movements, taking regular breaks can help prevent injury.
When to Seek Medical Attention
If you face any of the following symptoms, it may be time to consult a healthcare provider:
- Severe pain that doesn't improve with rest or medication.
- Inability to move your shoulder or arm without significant pain.
- Persistent swelling or deformity in the shoulder area.
Conclusion
Pain with internal rotation of the shoulder can significantly impact your quality of life and daily activities. Understanding the causes, recognizing the symptoms, and knowing when to seek treatment are essential steps in managing this condition effectively. Whether through conservative treatments, advanced interventions, or preventive strategies, addressing shoulder pain early can lead to a favorable recovery and a return to normal activities. Always consult with health professionals such as chiropractors or physical therapists, like those at IAOM-US, who can provide tailored advice and treatment plans for your specific situation.
Remember, a healthy shoulder is essential for a balanced and active lifestyle. Prioritizing shoulder health can pave the way for better physical functioning and overall well-being.